Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to create an updatable view and update data in the underlying table through the view.
Introduction to MySQL updatable views
In MySQL, views are not only query-able but also updatable. It means that you can use the INSERT or UPDATE statement to insert or update rows of the base table through the updatable view. In addition, you can use DELETE statement to remove rows of the underlying table through the view.
However, to create an updatable view, the SELECT statement that defines the view must not contain any of the following elements:
- Aggregate functions such as MIN, MAX, SUM, AVG, and COUNT.
- DISTINCT
- GROUP BY clause.
- HAVING clause.
- UNION or UNION ALL clause.
- Left join or outer join.
- Subquery in the SELECT clause or in the WHERE clause that refers to the table appeared in the FROM clause.
- Reference to non-updatable view in the FROM clause.
- Reference only to literal values.
- Multiple references to any column of the base table.
If you create a view with the TEMPTABLE algorithm, you cannot update the view.
Note that it is sometimes possible to create updatable views based on multiple tables using an inner join.
MySQL updatable view example
Let’s create an updatable view.
First, we create a view named officeInfo based on the offices table in the sample database. The view refers to three columns of the offices table:officeCode phone, and city.
CREATE VIEW officeInfo
AS
SELECT officeCode, phone, city
FROM offices;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
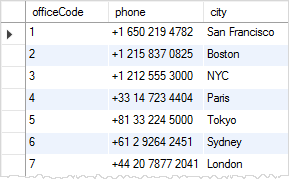
Next, we can query data from the officeInfo view using the following statement:
SELECT
*
FROM
officeInfo;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Then, we can change the phone number of the office with officeCode 4 through the officeInfo view using the following UPDATE statement.
UPDATE officeInfo
SET
phone = '+33 14 723 5555'
WHERE
officeCode = 4;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
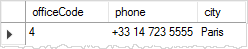
Finally, to verify the change, we can query the data from the officeInfo view by executing the following query:
SELECT
*
FROM
officeInfo
WHERE
officeCode = 4;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Checking updatable view information
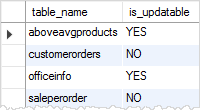
You can check if a view in a database in updatable by querying the is_updatable column from the views table in the information_schema database.
The following query gets all views from the classicmodels database and shows which views are updatable.
SELECT
table_name,
is_updatable
FROM
information_schema.views
WHERE
table_schema = 'classicmodels';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Removing rows through the view
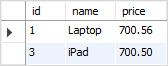
First, we create a table named items, insert some rows into the items table, and create a view that contains items whose prices are greater than 700.
-- create a new table named items
CREATE TABLE items (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
price DECIMAL(11 , 2 ) NOT NULL
);
-- insert data into the items table
INSERT INTO items(name,price)
VALUES('Laptop',700.56),('Desktop',699.99),('iPad',700.50) ;
-- create a view based on items table
CREATE VIEW LuxuryItems AS
SELECT
*
FROM
items
WHERE
price > 700;
-- query data from the LuxuryItems view
SELECT
*
FROM
LuxuryItems;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Second, we use the DELETE statement to remove a row with id value 3.
DELETE FROM LuxuryItems
WHERE
id = 3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
MySQL returns a message saying that 1 row(s) affected.
Third, let’s check the data through the view again.
SELECT
*
FROM
LuxuryItems;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
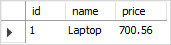
Fourth, we can also query the data from the base table items to verify if the DELETE statement actually deleted the row.
SELECT
*
FROM
items;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
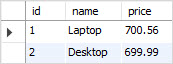
As you see, the row with id 3 was removed from the base table.
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to create an updatable view and update data in the underlying table through the view.